List of employees for example. Quick way to find duplicate values using LAG windowing function
;with c as (
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName],
[FirstName] + ' ' + [LastName] x
,[StaffNumber]
FROM Employee
),
cc as(
SELECT FirstName, LastName, StaffNumber, x , lag (x) over (partition by LastName order by x) dup
from c)
select FirstName, LastName, StaffNumber, x , dup From cc
where x=dup
order by LastName
Showing posts with label SQL. Show all posts
Showing posts with label SQL. Show all posts
Wednesday, 6 June 2018
Tuesday, 24 December 2013
List all Stored Procedures within a db - SQL
SELECT
*
FROM
TFSheffieldNew.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ROUTINES
WHERE
(ROUTINE_TYPE = 'PROCEDURE')
*
FROM
TFSheffieldNew.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ROUTINES
WHERE
(ROUTINE_TYPE = 'PROCEDURE')
Tuesday, 20 November 2012
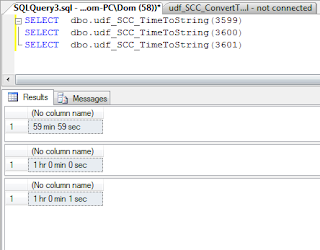
Convert time to string - SQL
Scenario where a db field contains seconds, the user wanted a SSRS report displaying various aggregates of the seconds field as Hours - Minutes - Seconds.
IFOBJECT_ID('dbo.udf_SCC_TimeToString') IS NOT NULL
DROP FUNCTION dbo.udf_SCC_TimeToString ;
GO
CREATEFUNCTION dbo.udf_SCC_TimeToString
(
@timesec INT) --input in seconds as integer
RETURNSVARCHAR(25)
/*==========================================
Dom Horton
17/10/2012
==========================================*/
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE
@return
AS VARCHAR(25),
@a AS INT,
@b AS INT,
@hours AS INT,
@mins AS INT,
@secs AS INT;
SET@a = @timesec%3600 --get no. of seconds over the hour
SET@hours = (@timesec - @a)/3600 --get no. of seconds of completed hours, divide by hour in seconds to get completed hours
SET@b = @a --hold no. of secs over the hour
SET@a = @b%60--get no. of secs over the min
SET@mins = (@b - @a)/60 --get no. of seconds of completed mins, divide by min in secs to get completed minutes
SET@secs = @a
SET@return =
CASE
WHEN @timesec >=3600
THEN
convert(varchar(10),@hours) + ' hr ' +
convert(varchar(10),@mins) + ' min ' +
convert(varchar(10),@secs) + ' sec '
WHEN @timesec >=60
THEN
convert(varchar(10),@mins) + ' min ' +
convert(varchar(10),@secs) + ' sec '
ELSE
convert(varchar(10),@secs) + ' sec '
END;
RETURN
@return
END
Example below showing the Stored Procedure in use:
and in use in a SSRS report:
IFOBJECT_ID('dbo.udf_SCC_TimeToString') IS NOT NULL
DROP FUNCTION dbo.udf_SCC_TimeToString ;
GO
CREATEFUNCTION dbo.udf_SCC_TimeToString
(
@timesec INT) --input in seconds as integer
RETURNSVARCHAR(25)
/*==========================================
Dom Horton
17/10/2012
==========================================*/
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE
@return
AS VARCHAR(25),
@a AS INT,
@b AS INT,
@hours AS INT,
@mins AS INT,
@secs AS INT;
SET@a = @timesec%3600 --get no. of seconds over the hour
SET@hours = (@timesec - @a)/3600 --get no. of seconds of completed hours, divide by hour in seconds to get completed hours
SET@b = @a --hold no. of secs over the hour
SET@a = @b%60--get no. of secs over the min
SET@mins = (@b - @a)/60 --get no. of seconds of completed mins, divide by min in secs to get completed minutes
SET@secs = @a
SET@return =
CASE
WHEN @timesec >=3600
THEN
convert(varchar(10),@hours) + ' hr ' +
convert(varchar(10),@mins) + ' min ' +
convert(varchar(10),@secs) + ' sec '
WHEN @timesec >=60
THEN
convert(varchar(10),@mins) + ' min ' +
convert(varchar(10),@secs) + ' sec '
ELSE
convert(varchar(10),@secs) + ' sec '
END;
RETURN
@return
END
Example below showing the Stored Procedure in use:
and in use in a SSRS report:
Labels:
Convert time to string,
Date and Time,
Datepart,
Mod,
Modular,
SQL,
SSRS,
Stored Procedures,
String,
Time,
Time to String
Thursday, 6 September 2012
Missing indexes - SQL
SELECT index_handle, database_id, object_id, equality_columns, inequality_columns, included_columns, statement
FROM sys.dm_db_missing_index_details
FROM sys.dm_db_missing_index_details
Index usage - SQL
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(I.object_id) AS TableName, I.name, I.index_id, I.type_desc, I.is_unique,
I.fill_factor, I.is_padded, I.is_disabled, I.is_hypothetical,
IUS.index_id , IUS.user_seeks, IUS.user_scans, IUS.user_lookups, IUS.user_updates, IUS.last_user_seek,
IUS.last_user_scan, IUS.last_user_lookup, IUS.last_user_update, IUS.system_seeks, IUS.system_scans, IUS.system_lookups, IUS.system_updates,
IUS.last_system_seek, IUS.last_system_scan, IUS.last_system_lookup, IUS.last_system_update
FROM sys.indexes AS I LEFT OUTER JOIN
sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats AS IUS
ON I.object_id = IUS.object_id AND
I.index_id = IUS.index_id
ORDER BY OBJECT_NAME(I.object_id)
I.fill_factor, I.is_padded, I.is_disabled, I.is_hypothetical,
IUS.index_id , IUS.user_seeks, IUS.user_scans, IUS.user_lookups, IUS.user_updates, IUS.last_user_seek,
IUS.last_user_scan, IUS.last_user_lookup, IUS.last_user_update, IUS.system_seeks, IUS.system_scans, IUS.system_lookups, IUS.system_updates,
IUS.last_system_seek, IUS.last_system_scan, IUS.last_system_lookup, IUS.last_system_update
FROM sys.indexes AS I LEFT OUTER JOIN
sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats AS IUS
ON I.object_id = IUS.object_id AND
I.index_id = IUS.index_id
ORDER BY OBJECT_NAME(I.object_id)
Wednesday, 9 March 2011
Return a random row - SQL
Instead of using the RAND() function which I believe is not truly random since using the same seed value results in the same output:
Whereas, CHECKSUM(NEWID()) would work:
and can thus be used to return a random row:
SELECT TOP(1) School.SchoolNameFROM School
ORDER BY CHECKSUM(NEWID());
Whereas, CHECKSUM(NEWID()) would work:
and can thus be used to return a random row:
ORDER BY CHECKSUM(NEWID());
Tuesday, 4 January 2011
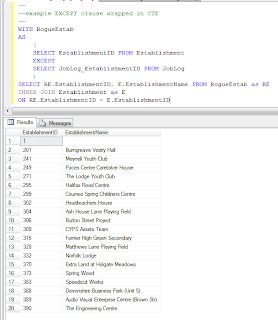
Using the EXCEPT clause wrapped in a CTE - SQL
--
--example EXCEPT clause wrapped in CTE
--
WITH RogueEstab
AS
(
SELECT EstablishmentID FROM Establishment
EXCEPT
SELECT JobLog_EstablishmentID FROM JobLog
)
SELECT RE.EstablishmentID, E.EstablishmentName FROM RogueEstab AS RE
INNER JOIN Establishment AS E
ON RE.EstablishmentID = E.EstablishmentID
--example EXCEPT clause wrapped in CTE
--
WITH RogueEstab
AS
(
SELECT EstablishmentID FROM Establishment
EXCEPT
SELECT JobLog_EstablishmentID FROM JobLog
)
SELECT RE.EstablishmentID, E.EstablishmentName FROM RogueEstab AS RE
INNER JOIN Establishment AS E
ON RE.EstablishmentID = E.EstablishmentID
Using the EXCEPT clause - SQL
--
--example EXCEPT clause....lists EstablishmentID without corresponding Jobs
--
SELECT EstablishmentID FROM Establishment
EXCEPT
SELECT JobLog_EstablishmentID FROM JobLog
--example EXCEPT clause....lists EstablishmentID without corresponding Jobs
--
SELECT EstablishmentID FROM Establishment
EXCEPT
SELECT JobLog_EstablishmentID FROM JobLog
ORDER BY EstablishmentID
Using the OVER clause - SQL
--
--using OVER clause to get count of SubTypes
--
SELECT E.EstablishmentName, S.JobSubTypeDescription
,COUNT(*) OVER(PARTITION BY S.JobSubTypeDescription) AS nums
FROM Establishment AS E LEFT OUTER JOIN
JobLog AS J ON E.EstablishmentID=J.JobLog_EstablishmentID INNER JOIN
JobSubType AS S ON J.JobLog_JobSubTypeID=S.JobSubTypeID
ORDER BY E.EstablishmentName
--using OVER clause to get count of SubTypes
--
SELECT E.EstablishmentName, S.JobSubTypeDescription
,COUNT(*) OVER(PARTITION BY S.JobSubTypeDescription) AS nums
FROM Establishment AS E LEFT OUTER JOIN
JobLog AS J ON E.EstablishmentID=J.JobLog_EstablishmentID INNER JOIN
JobSubType AS S ON J.JobLog_JobSubTypeID=S.JobSubTypeID
ORDER BY E.EstablishmentName
Tuesday, 23 November 2010
Create a list of dates on the fly - SQL
I've recently had the requirement to produce a list of the last 30 days on the fly (I didn't have the option to refer to a 'Numbers' table). This was to be used as a 'Command' in Crystal Reports and joined to a database table to produce 'missing dates'.
Using the system table, spt_values, the first stage was to produce a list of numbers:
SELECT number AS rn FROM master.dbo.spt_values
WHERE type = 'P' AND number BETWEEN 0 AND 29
This is then extended to produce a list of the last 30 dates.
SELECT DATEADD(dd, -D.rn, DATEADD(dd, DATEDIFF(dd,0,GETDATE()), 0)) AS ReportDate
FROM (
SELECT number AS rn FROM master.dbo.spt_values
WHERE type = 'P' AND number BETWEEN 0 AND 29
) AS D
This was with help from both Chris Morris & Kevin McKelvey at http://www.sqlservercentral.com/
CTE solution here
Using the system table, spt_values, the first stage was to produce a list of numbers:
SELECT number AS rn FROM master.dbo.spt_values
WHERE type = 'P' AND number BETWEEN 0 AND 29
This is then extended to produce a list of the last 30 dates.
SELECT DATEADD(dd, -D.rn, DATEADD(dd, DATEDIFF(dd,0,GETDATE()), 0)) AS ReportDate
FROM (
SELECT number AS rn FROM master.dbo.spt_values
WHERE type = 'P' AND number BETWEEN 0 AND 29
) AS D
This was with help from both Chris Morris & Kevin McKelvey at http://www.sqlservercentral.com/
CTE solution here
Labels:
Auxiliary,
Crystal Reports,
DateAdd,
DateDiff,
Dates,
GetDate,
List of dates,
Missing Dates,
SQL
Wednesday, 10 November 2010
Column aliases and derived tables in TSQL 2005 - SQL
SELECT YearMonth, COUNT(JobLogID) AS JobCount
FROM
(SELECT JobLogID, CONVERT(VARCHAR(7), JobLogSignOffTimeStamp, 121) AS YearMonth
FROM JobLog WHERE JobLogSignOff ='1') AS J
GROUP BY YearMonth
ORDER BY YearMonth;
FROM
(SELECT JobLogID, CONVERT(VARCHAR(7), JobLogSignOffTimeStamp, 121) AS YearMonth
FROM JobLog WHERE JobLogSignOff ='1') AS J
GROUP BY YearMonth
ORDER BY YearMonth;
Monday, 1 November 2010
Row numbering in TSQL 2005 - SQL
New to SQL Server 2005 is ROW_NUMBER function.
SELECT
JobLog.JobLogID,
Establishment.EstablishmentName,
JobSubType.JobSubTypeDescription,
JobLog.JobLogSignOffTimeStamp,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY EstablishmentName ) AS rownumNonDeterministic,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY EstablishmentName,JobLog.JobLogSignOffTimeStamp ) AS rownumDeterministic,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY EstablishmentName ORDER BY EstablishmentName,JobLog.JobLogSignOffTimeStamp ) AS rownumPartitioning
FROM JobLog
INNER JOIN
Establishment ON JobLog.JobLog_EstablishmentID = Establishment.EstablishmentID
INNER JOIN
JobSubType ON JobLog.JobLog_JobSubTypeID = JobSubType.JobSubTypeID
WHERE JobLog.JobLogSignOff = '1'
ORDER BY EstablishmentName,JobLog.JobLogSignOffTimeStamp
SELECT
JobLog.JobLogID,
Establishment.EstablishmentName,
JobSubType.JobSubTypeDescription,
JobLog.JobLogSignOffTimeStamp,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY EstablishmentName ) AS rownumNonDeterministic,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY EstablishmentName,JobLog.JobLogSignOffTimeStamp ) AS rownumDeterministic,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY EstablishmentName ORDER BY EstablishmentName,JobLog.JobLogSignOffTimeStamp ) AS rownumPartitioning
FROM JobLog
INNER JOIN
Establishment ON JobLog.JobLog_EstablishmentID = Establishment.EstablishmentID
INNER JOIN
JobSubType ON JobLog.JobLog_JobSubTypeID = JobSubType.JobSubTypeID
WHERE JobLog.JobLogSignOff = '1'
ORDER BY EstablishmentName,JobLog.JobLogSignOffTimeStamp
Friday, 3 September 2010
Useful date formulas - SQL
This was posted on http://www.sqlservercentral.com/blogs/lynnpettis/archive/2009/03/25/some-common-date-routines.aspx
declare @ThisDate datetime;
set @ThisDate = getdate();
select dateadd(dd, datediff(dd, 0, @ThisDate), 0) -- Beginning of this day
select dateadd(dd, datediff(dd, 0, @ThisDate) + 1, 0) -- Beginning of next day
select dateadd(dd, datediff(dd, 0, @ThisDate) - 1, 0) -- Beginning of previous day
select dateadd(wk, datediff(wk, 0, @ThisDate), 0) -- Beginning of this week (Monday)
select dateadd(wk, datediff(wk, 0, @ThisDate) + 1, 0) -- Beginning of next week (Monday)
select dateadd(wk, datediff(wk, 0, @ThisDate) - 1, 0) -- Beginning of previous week (Monday)
select dateadd(mm, datediff(mm, 0, @ThisDate), 0) -- Beginning of this month
select dateadd(mm, datediff(mm, 0, @ThisDate) + 1, 0) -- Beginning of next month
select dateadd(mm, datediff(mm, 0, @ThisDate) - 1, 0) -- Beginning of previous month
select dateadd(qq, datediff(qq, 0, @ThisDate), 0) -- Beginning of this quarter (Calendar)
select dateadd(qq, datediff(qq, 0, @ThisDate) + 1, 0) -- Beginning of next quarter (Calendar)
select dateadd(qq, datediff(qq, 0, @ThisDate) - 1, 0) -- Beginning of previous quarter (Calendar)
select dateadd(yy, datediff(yy, 0, @ThisDate), 0) -- Beginning of this year
select dateadd(yy, datediff(yy, 0, @ThisDate) + 1, 0) -- Beginning of next year
select dateadd(yy, datediff(yy, 0, @ThisDate) - 1, 0) -- Beginning of previous year
declare @ThisDate datetime;
set @ThisDate = getdate();
select dateadd(dd, datediff(dd, 0, @ThisDate), 0) -- Beginning of this day
select dateadd(dd, datediff(dd, 0, @ThisDate) + 1, 0) -- Beginning of next day
select dateadd(dd, datediff(dd, 0, @ThisDate) - 1, 0) -- Beginning of previous day
select dateadd(wk, datediff(wk, 0, @ThisDate), 0) -- Beginning of this week (Monday)
select dateadd(wk, datediff(wk, 0, @ThisDate) + 1, 0) -- Beginning of next week (Monday)
select dateadd(wk, datediff(wk, 0, @ThisDate) - 1, 0) -- Beginning of previous week (Monday)
select dateadd(mm, datediff(mm, 0, @ThisDate), 0) -- Beginning of this month
select dateadd(mm, datediff(mm, 0, @ThisDate) + 1, 0) -- Beginning of next month
select dateadd(mm, datediff(mm, 0, @ThisDate) - 1, 0) -- Beginning of previous month
select dateadd(qq, datediff(qq, 0, @ThisDate), 0) -- Beginning of this quarter (Calendar)
select dateadd(qq, datediff(qq, 0, @ThisDate) + 1, 0) -- Beginning of next quarter (Calendar)
select dateadd(qq, datediff(qq, 0, @ThisDate) - 1, 0) -- Beginning of previous quarter (Calendar)
select dateadd(yy, datediff(yy, 0, @ThisDate), 0) -- Beginning of this year
select dateadd(yy, datediff(yy, 0, @ThisDate) + 1, 0) -- Beginning of next year
select dateadd(yy, datediff(yy, 0, @ThisDate) - 1, 0) -- Beginning of previous year
Thursday, 2 September 2010
Table metadata - SQL
Useful bit of code to get a tables metadata:
SELECT
COLUMN_NAME, TABLE_CATALOG, TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME, COLUMN_NAME AS Expr1, ORDINAL_POSITION, COLUMN_DEFAULT, IS_NULLABLE, DATA_TYPE, CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH, CHARACTER_OCTET_LENGTH, NUMERIC_PRECISION, NUMERIC_PRECISION_RADIX, NUMERIC_SCALE, DATETIME_PRECISION, CHARACTER_SET_CATALOG, CHARACTER_SET_SCHEMA, CHARACTER_SET_NAME, COLLATION_CATALOG, COLLATION_SCHEMA, COLLATION_NAME, DOMAIN_CATALOG, DOMAIN_SCHEMA, DOMAIN_NAME
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS
WHERE (TABLE_NAME = 'mytable')
ORDER BY ORDINAL_POSITION
SELECT
COLUMN_NAME, TABLE_CATALOG, TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME, COLUMN_NAME AS Expr1, ORDINAL_POSITION, COLUMN_DEFAULT, IS_NULLABLE, DATA_TYPE, CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH, CHARACTER_OCTET_LENGTH, NUMERIC_PRECISION, NUMERIC_PRECISION_RADIX, NUMERIC_SCALE, DATETIME_PRECISION, CHARACTER_SET_CATALOG, CHARACTER_SET_SCHEMA, CHARACTER_SET_NAME, COLLATION_CATALOG, COLLATION_SCHEMA, COLLATION_NAME, DOMAIN_CATALOG, DOMAIN_SCHEMA, DOMAIN_NAME
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS
WHERE (TABLE_NAME = 'mytable')
ORDER BY ORDINAL_POSITION
Labels:
Columns,
INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS,
metadata,
SQL
Tuesday, 17 August 2010
Auxiliary Calendar table - SQL
This code is derived from a useful article by Todd Fifield at SQLServerCentral.com and has been modified to include columns based on the ISO8601 date and times standard (here and here).
IF OBJECT_ID('dbo.CalendarDay') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.CalendarDay;
GO
CREATE TABLE CalendarDay
( DayID INT IDENTITY(1, 1)
, DayDate SMALLDATETIME
, WeekNumber INT
, OrdinalDate VARCHAR(8)
, DateWeekNumber VARCHAR(10)
, DayNumber INT
, NameOfDay VARCHAR(10)
)
GO
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE
@Date SMALLDATETIME;
SET DATEFIRST 1; --assuming start of week is monday
SET @Date = '2010-01-01';
WHILE @Date < '2011-01-01'
BEGIN
INSERT INTO CalendarDay
( DayDate, WeekNumber, OrdinalDate, DateWeekNumber, DayNumber, NameOfDay )
SELECT @Date
, (DATEPART(WK, @Date))
, CAST(DATEPART(YEAR, @Date) as VARCHAR) + '-' + CAST(DATEPART(DY, @Date) as VARCHAR)
, CAST(DATEPART(YEAR, @Date) as VARCHAR) + '-'
+ 'W' + CAST(DATEPART(WK, @Date) as VARCHAR) + '-'
+ CAST(DATEPART(WEEKDAY, @Date) as VARCHAR)
, DATEPART(WEEKDAY, @Date)
, CASE DATEPART(WEEKDAY, @Date)
WHEN 1 THEN 'Monday'
WHEN 2 THEN 'Tuesday'
WHEN 3 THEN 'Wednesday'
WHEN 4 THEN 'Thursday'
WHEN 5 THEN 'Friday'
WHEN 6 THEN 'Saturday'
ELSE 'Sunday' END;
SET @Date = DATEADD(day, 1, @Date);
END
GO
IF OBJECT_ID('dbo.CalendarDay') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.CalendarDay;
GO
CREATE TABLE CalendarDay
( DayID INT IDENTITY(1, 1)
, DayDate SMALLDATETIME
, WeekNumber INT
, OrdinalDate VARCHAR(8)
, DateWeekNumber VARCHAR(10)
, DayNumber INT
, NameOfDay VARCHAR(10)
)
GO
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE
@Date SMALLDATETIME;
SET DATEFIRST 1; --assuming start of week is monday
SET @Date = '2010-01-01';
WHILE @Date < '2011-01-01'
BEGIN
INSERT INTO CalendarDay
( DayDate, WeekNumber, OrdinalDate, DateWeekNumber, DayNumber, NameOfDay )
SELECT @Date
, (DATEPART(WK, @Date))
, CAST(DATEPART(YEAR, @Date) as VARCHAR) + '-' + CAST(DATEPART(DY, @Date) as VARCHAR)
, CAST(DATEPART(YEAR, @Date) as VARCHAR) + '-'
+ 'W' + CAST(DATEPART(WK, @Date) as VARCHAR) + '-'
+ CAST(DATEPART(WEEKDAY, @Date) as VARCHAR)
, DATEPART(WEEKDAY, @Date)
, CASE DATEPART(WEEKDAY, @Date)
WHEN 1 THEN 'Monday'
WHEN 2 THEN 'Tuesday'
WHEN 3 THEN 'Wednesday'
WHEN 4 THEN 'Thursday'
WHEN 5 THEN 'Friday'
WHEN 6 THEN 'Saturday'
ELSE 'Sunday' END;
SET @Date = DATEADD(day, 1, @Date);
END
GO
Labels:
Auxiliary,
Calendar table,
Cast,
CREATE TABLE,
Date and Time,
DateAdd,
Datepart,
Dates,
DROP TABLE,
DY,
ISO 8601,
SQL,
Weekday,
WK,
Year
Tuesday, 10 August 2010
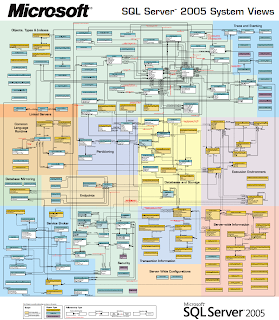
SQL Server 2005 System Views
Here's a very useful schema showing SQL Server 2005 System Views:
Labels:
SQL,
SQL Server 2005,
SQL Server 2005 System Views,
System Views,
Views
Tuesday, 22 June 2010
Show Database name - SQL
To show the database name:
SELECT DB_NAME() AS DataBaseName
This also proves useful in Crystal Report development where 'test' and 'live' databases in use. Simply add the above code to a Command in Database Expert and show the DatabaseName field in the report header.
SELECT DB_NAME() AS DataBaseName
This also proves useful in Crystal Report development where 'test' and 'live' databases in use. Simply add the above code to a Command in Database Expert and show the DatabaseName field in the report header.
Saturday, 29 May 2010
Auxiliary Months of Year Table - SQL
IF OBJECT_ID('dbo.CalendarMonth') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.CalendarMonth;
GO
CREATE TABLE dbo.CalendarMonth
(
mon nvarchar(10) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO dbo.CalendarMonth(mon)
SELECT 'January ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'February ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'March ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'April ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'May ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'June ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'July ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'August ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'September ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'October ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'November ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'December '
If, for example you are trying to provide an output of sales data for every month and the sale table doesn't have records for all 12 months, by creating an OUTER JOIN to the Calendar table, each month is returned.
IF OBJECT_ID('dbo.yearsales') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.yearsales;
GO
CREATE TABLE dbo.yearsales
(
sales int NOT NULL,saledate smalldatetime NOT NULL
)
INSERT INTO dbo.yearsales (sales, saledate)
SELECT '4','Jan 1 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '5','Feb 1 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '1','Apr 3 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '11','May 5 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '1','Jun 15 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '4','Aug 5 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '3','Oct 12 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '17','Nov 2 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '19','Dec 14 2009 12:00AM'
SELECT yearsales.sales, yearsales.saledate, DATENAME(month, yearsales.saledate) AS salesmonthname, CalendarMonth.mon
FROM yearsales RIGHT OUTER JOINCalendarMonth ON DATENAME(month, yearsales.saledate) = CalendarMonth.mon
DROP TABLE dbo.CalendarMonth;
GO
CREATE TABLE dbo.CalendarMonth
(
mon nvarchar(10) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO dbo.CalendarMonth(mon)
SELECT 'January ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'February ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'March ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'April ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'May ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'June ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'July ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'August ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'September ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'October ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'November ' UNION ALL
SELECT 'December '
If, for example you are trying to provide an output of sales data for every month and the sale table doesn't have records for all 12 months, by creating an OUTER JOIN to the Calendar table, each month is returned.
IF OBJECT_ID('dbo.yearsales') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.yearsales;
GO
CREATE TABLE dbo.yearsales
(
sales int NOT NULL,saledate smalldatetime NOT NULL
)
INSERT INTO dbo.yearsales (sales, saledate)
SELECT '4','Jan 1 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '5','Feb 1 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '1','Apr 3 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '11','May 5 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '1','Jun 15 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '4','Aug 5 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '3','Oct 12 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '17','Nov 2 2009 12:00AM' UNION ALL
SELECT '19','Dec 14 2009 12:00AM'
SELECT yearsales.sales, yearsales.saledate, DATENAME(month, yearsales.saledate) AS salesmonthname, CalendarMonth.mon
FROM yearsales RIGHT OUTER JOINCalendarMonth ON DATENAME(month, yearsales.saledate) = CalendarMonth.mon
Wednesday, 26 May 2010
Datetime types in SQL - SQL
You cannot store only the date or time portion.
If only the date is specified, 00:00:00.000 is stored in the time portion.
If only the time is specified, 1900-01-01 is stored in the date portion.
For example,
SELECT CAST ('20100526' as datetime)
SELECT CAST ('12:47:59:009' as datetime)
Friday, 9 April 2010
Useful Character code chart
Here's a link to a useful character code chart:
http://tlt.its.psu.edu/suggestions/international/bylanguage/mathchart.html
and to get the Windows Character Map Utility:
Start>>Programs>>Accessories>>System Tools
and simply copy and paste the relevant character or obtain the unicode number from the keystoke value, where applicable, or convert the hex to decimal.
Hexadecimal to decimal converter:
http://easycalculation.com/hex-converter.php
http://tlt.its.psu.edu/suggestions/international/bylanguage/mathchart.html
and to get the Windows Character Map Utility:
Start>>Programs>>Accessories>>System Tools
and simply copy and paste the relevant character or obtain the unicode number from the keystoke value, where applicable, or convert the hex to decimal.
Hexadecimal to decimal converter:
http://easycalculation.com/hex-converter.php
Labels:
Char,
Character Codes,
Chr,
CR,
Crystal Reports,
decimal,
hexadecimal,
SQL,
SQL Server Reporting Services,
Unicode
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)